All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the MDS Alliance.
The mds Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the mds Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The mds and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View MDS content recommended for you
CPX-351 versus FLAG-Ida in patients with adverse karyotype AML and high-risk MDS: Analysis from NCRI AML19 trial
Patients diagnosed with adverse karyotype acute myeloid leukemia (AML) typically experience lower response rates, a higher risk of refractory disease, and shorter durations of remission.1 The current standard induction strategy is the 7 + 3 regimen of daunorubicin and cytarabine; however, more recently, an increasing proportion of patients are eligible for CPX-351 therapy due to the revised risk classification and a greater overlap between high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities and those considered to be myelodysplasia related.1 CPX-351 is a liposomal formulation of cytarabine + daunorubicin at an optimally synergistic 5:1 ratio.1 A phase II study (NCT00788892) demonstrated higher response rates and overall survival with CPX-351 compared with the 7 + 3 regimen, subsequently leading to its approval for use in younger as well as older patients diagnosed with secondary AML.1
Currently, the clinical benefit of CPX-351 has yet to be explored in patients diagnosed with AML with myelodysplasia-related mutations, such as ASXL1, BCOR, EZH2, SF3B1, and SRSF2. Recently, Othman et al.1 published results from the AML19 trial (ISRCTN78449203) evaluating CPX-351 versus FLAG-Ida (fludarabine + cytarabine + granulocyte-colony stimulating factor + idarubicin) in younger patients with high-risk AML and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). The AML Hub has previously reported on the AML19 trial, including an interview with Nigel Russel from the 4th National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI) AML Academy Meeting. Here, we are pleased to summarize the key findings.1
Study design
- Patients were randomized 2:1 in favor of CPX-351 (Figure 1).
- Patients were stratified by age group, performance status, and disease type.
Figure 1. Study design*
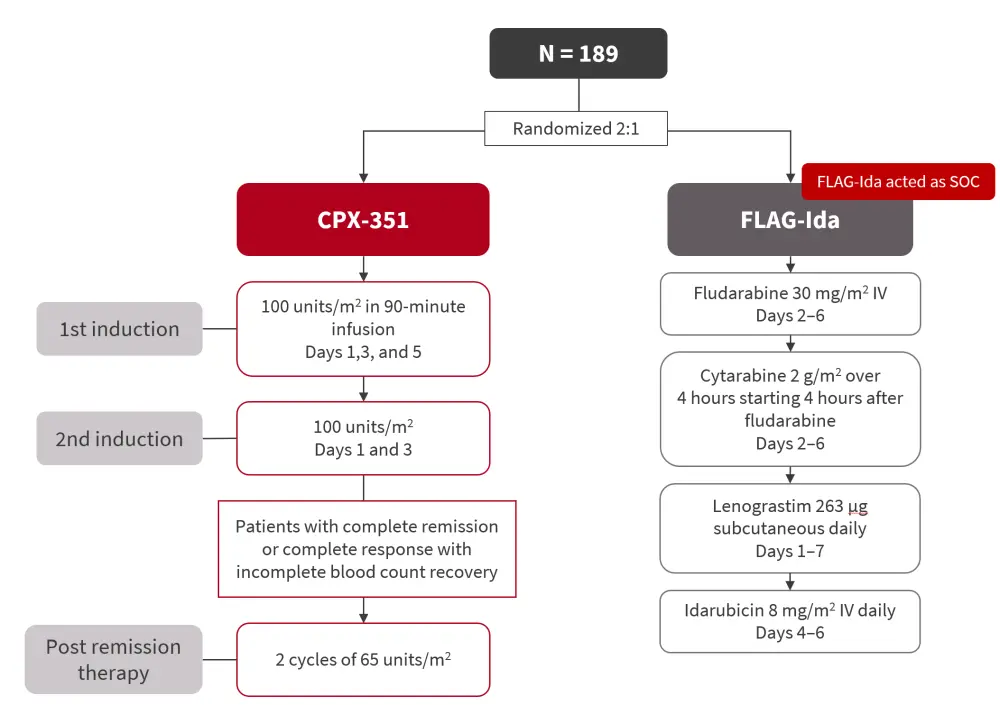
FLAG-Ida, fludarabine + cytarabine + granulocyte-colony stimulating factor + idarubicin; IV, intravenous; SOC, standard of care.
*Adapted from Othman, et al.1
Results
- The baseline patient characteristics are shown in Table 1.
- A large proportion of patients had mutations in >1 MDS related gene.
Table 1. Baseline patient characteristics*
|
AML, acute myeloid leukemia; ELN, European LeukemiaNet; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; FLAG-Ida, fludarabine + cytarabine + granulocyte-colony stimulating factor + idarubicin; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; WHO, World Health Organization. |
||
|
Characteristic, % (unless otherwise stated) |
FLAG-IDA (n = 82) |
CPX-351 (n = 105) |
|---|---|---|
|
Median age (range), years |
55 (18–67) |
57 (23–70) |
|
Female |
41 |
43 |
|
Diagnosis |
||
|
De novo AML |
51 |
48 |
|
Secondary AML |
21 |
20 |
|
High-risk MDS |
28 |
32 |
|
Cytogenetics + FISH |
||
|
Complex ≥3 abnormalities |
54 |
50 |
|
Complex ≥4 abnormalities |
51 |
48 |
|
−5/del5q/add5q |
40 |
43 |
|
−7/del7q/add7q |
45 |
44 |
|
−17/abn17p |
15 |
24 |
|
11q23 |
8 |
7.7 |
|
3q21 |
4 |
5.8 |
|
MDS-related cytogenetics (WHO 2016) |
75 |
71 |
|
Cytogenetic risk group |
||
|
Adverse |
84 |
83 |
|
Intermediate |
13 |
16 |
|
Missing/failed |
2 |
1 |
|
Mutations |
||
|
TP53 |
43 |
45 |
|
Mutation in MDS-related gene† |
51 |
29 |
|
AML/MDS with MDS-related gene mutation (without co-mutation in TP53)† |
39 |
31 |
|
1 mutated MDS-related gene† |
14 |
8 |
|
≥2 mutated MDS-related genes† |
26 |
23 |
|
NPM1 |
2 |
4 |
|
FLT3 TKD |
1 |
1 |
|
FLT3 ITD |
5 |
4 |
|
ELN 2022 risk group |
||
|
Adverse |
95 |
94 |
|
Intermediate |
4 |
5 |
|
Missing |
1 |
1 |
Induction response and survival outcomes
A trend towards higher overall response rates was observed in patients treated with FLAG-Ida compared with CPX-351 (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Overall response rates after induction Cycles 1 and 2*
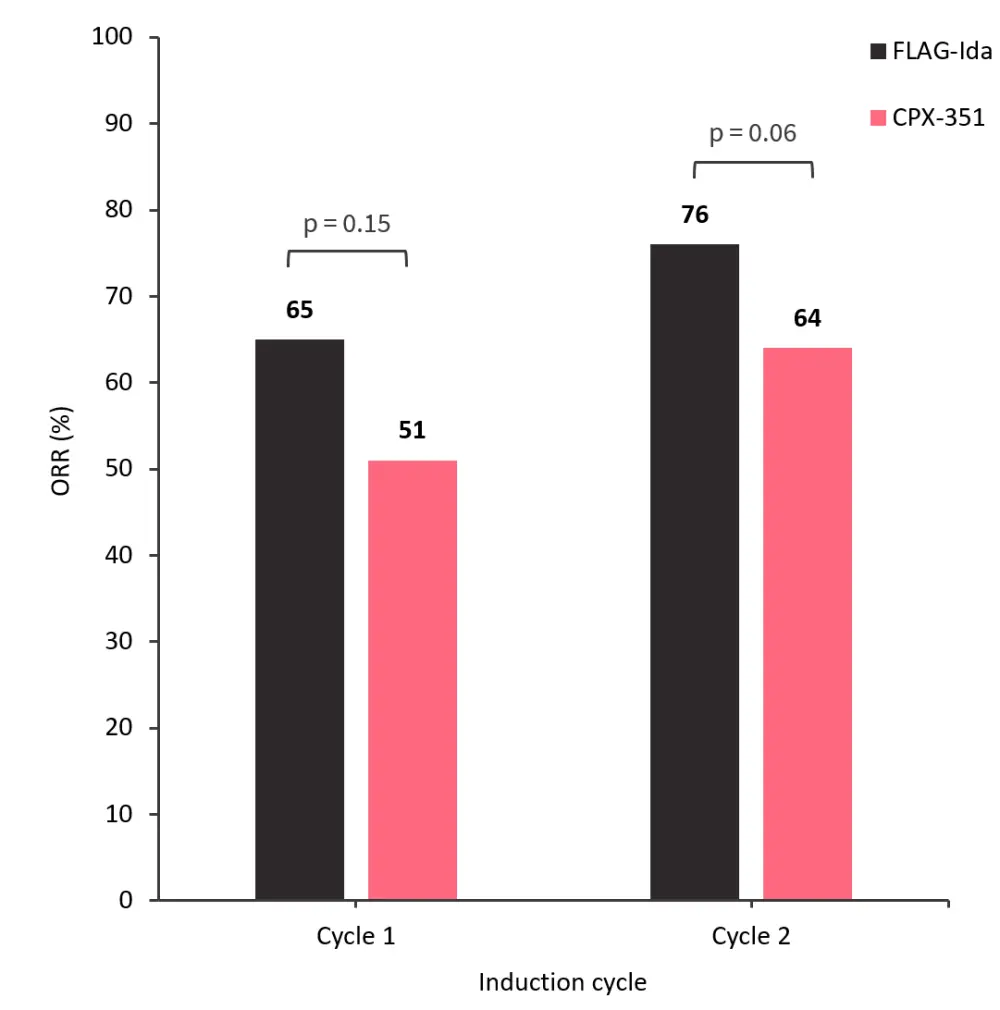
FLAG-Ida, fludarabine + cytarabine + granulocyte-colony stimulating factor + idarubicin; ORR, overall response rate.
*Adapted from Othman, et al.1
- The median overall survival (OS) was 13.3 versus 11.4 months in the CPX-351 and FLAG-Ida groups (p = 0.36).
- The 3-year OS rate was 32% versus 25% in the CPX-351 and FLAG-Ida groups (p = 0.36).
- Event free survival was not significantly different between the CPX-351 and FLAG-Ida groups (p = 0.86).
- The median relapse free survival in the CPX-351 group was 22.1 months compared with 8.35 months in the FLAG-Ida group (p = 0.08)
- The 3-year relapse free survival rate was 39% vs 29% in the CPX-351 and FLAG-Ida groups, respectively (p = 0.08).
- Although a greater number of patients treated with CPX-351 were transplanted, this did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.41).
- Survival did not differ depending on the induction regimen used.
- Day 30 and Day 60 mortality rates were similar between both treatment groups (p = 0.46 and p = 0.77, respectively).
- The cumulative incidence of death in remission censored at transplantation was higher in patients treated with FLAG-Ida.
Outcomes according to patient subgroup
- In patients with secondary AML, no difference in OS was observed between the CPX-351 and FLAG-Ida groups (hazard ratio [HR], 1; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.59–1.69).
- Similarly, patients diagnosed with secondary AML with myelodysplasia-related cytogenetic abnormalities experienced no difference in OS across both groups (HR, 0.94; 95% CI, 0.28–1).
- On the contrary, patients diagnosed with mutationally defined secondary AML/MDS experienced significantly longer OS with CPX-351 versus FLAG-Ida (38.4 months vs 16.3 months; p = 0.05).
- These patients had a similar ORR (70% vs 62%; p = 0.5), but no decrease in relapse.
- There was a trend towards longer OS with CPX-351 treatment in patients with high-risk MDS.
Measurable residual disease
- Bone marrow minimal residual disease (MRD) results were available in 59 patients, of which 37% achieved an MRD response.
- Median OS was longer in patients who had an MRD response compared with those who did not (24.3 vs 8.4 months).
- MRD response was higher in patients treated with FLAG-Ida versus patients treated with CPX-351 (55% vs 28%).
- In patients with MDS-related gene mutations, MRD response was similar in both CPX-351 and FLAG-Ida groups (33% vs 36%).
Safety
- In Course 1, the median days required for platelet recovery (>100 ×109/L) was longer in patients treated with CPX-351 versus FLAG-Ida (34 vs 29 days; p < 0.001).
- There was no difference between CPX-351 and FLAG-Ida groups in neutrophil recovery (1 ×109/L; p = 0.11).
- After Course 2, there were significantly fewer patients showing an improvement in platelet and neutrophil recovery.
- In patients who showed improvement, time to recovery was significantly delayed versus those who did not show recovery (neutrophils, 46 vs 31 days; p = 0.002; platelets, 36 vs 31 days; p = 0.19).
- Overall, Grade ≥3 non-hematological toxicities were similar between CPX-351 and FLAG-Ida groups (18% vs 21%).
Conclusion
Overall, there was a significant survival benefit with CPX-351 therapy for patients diagnosed with de novo AML defined by the presence of MDS-related mutations. On the contrary, there was no clinical advantage with CPX-351 compared to FLAG-Ida in patients diagnosed with secondary AML. Although these findings require validation in future prospective studies, they provide important rationale for the use of CPX-351 and the need for comprehensive next-generation sequencing results prior to treatment initiation.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content

